
In contrast, the snprintf() function is designed with safety in mind. Writing too much data to the allocated space can lead to issues such as memory corruption or even security threats. The traditional sprintf() function lacks built-in protection against buffer overflows. The final string is: Ascii value difference of s and a is 18Īs briefly mentioned above, the main distinction between these two functions is how they deal with buffer overflow situations. The result should be the following output: The length of the buffer is: 39

Return 0 to indicate the program executed successfully Printf("The final string is: %s", buffer)

Printf("The length of the buffer is: %d\n", buffer_length) Int buffer_length = sprintf(buffer, "Ascii value difference of %c and %c is %d", char1, char2, difference) Store the return value (number of characters written to the buffer) in an integer variable Assign a formatted string to the buffer using sprintf function Calculate the ASCII value difference between the two characters Declare and initialize character variables for comparison
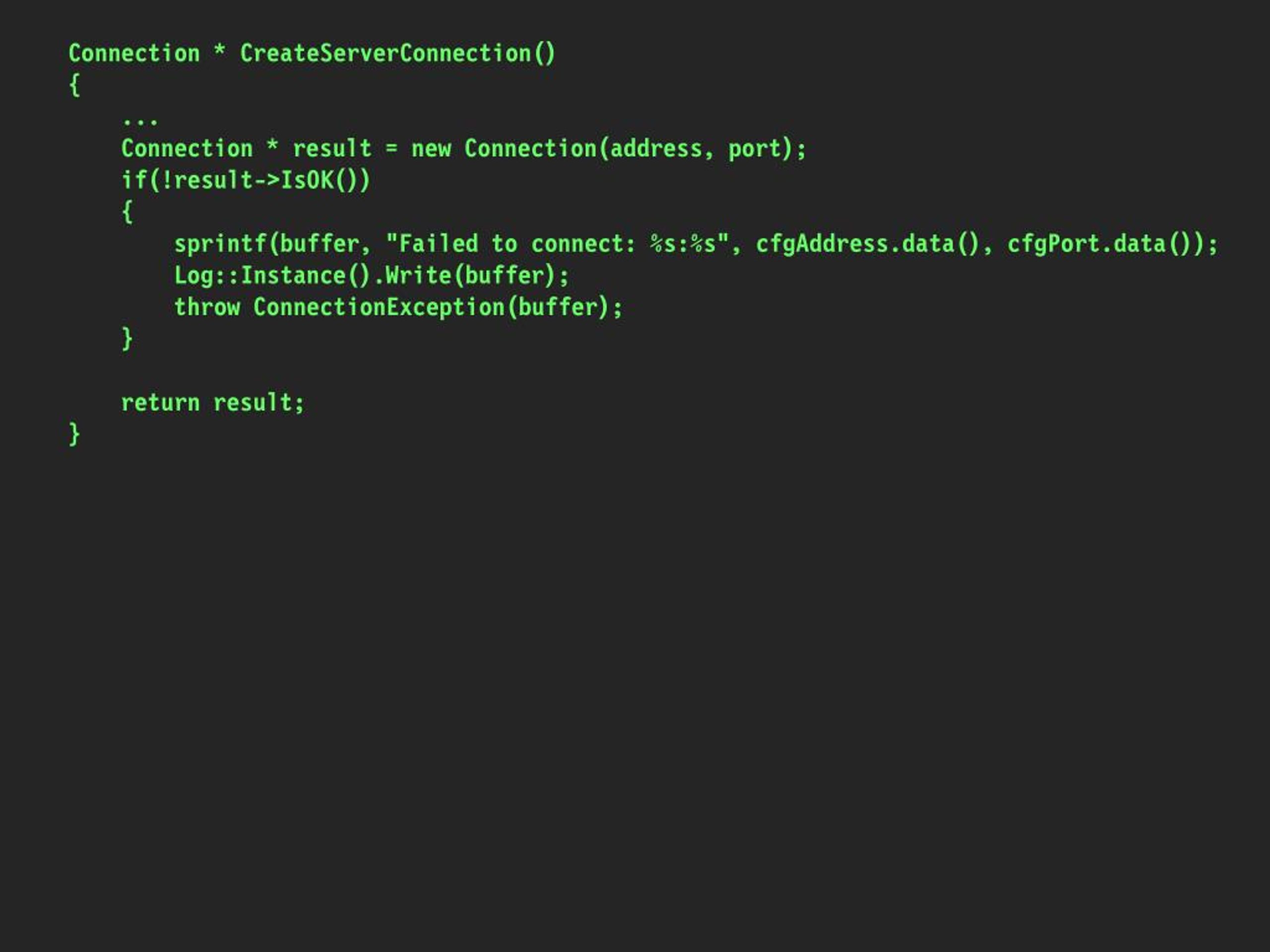
#Sprintf buffer overflow code#
Code exampleīelow is an example demonstrating the usage of the sprintf() function in C: #include For example, if the execution fails because the output was bigger than the available buffer, sprintf returns a negative value. If the function executes successfully, it returns the number of characters written to the buffer, excluding the terminating null character. The return type of the sprintf function is int. It follows the same specifications as print(). format-a C string that defines the output format, including placeholders for the integer arguments to be inserted in the formatted string.str-a character array where data will be written.Here is the general syntax of the sprintf function: int sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ) Īs you can see it had three types of parameters: Generating unique IDs or filenames: If you need to generate unique IDs or filenames based on specific patterns, you can use sprintf to format the values according to the desired pattern.Date and time formatting: You can use sprintf to format date and time values based on the current system time or other timestamp values.Creating file paths: When constructing file paths dynamically based on user input or other variables, you can use sprintf to format the directory path, file name, and extension.Floating-point number formatting: sprintf can be used to format floating-point numbers with a specific number of decimal places or in scientific notation.Formatting strings with variables: When you need to create a formatted string that includes variables or other data, you can use sprintf to insert the values into the desired positions in the string.To give a general sense of what the function does, here are examples of how it is commonly used: Common Use Cases for the sprint() Function The similar snprintf the function is more secure because it uses an extra parameter-the maximum number of characters for the output string that can prevent this issue. The concern with the sprintf function is that, when not utilized properly, it can lead to buffer overflows. print the formatted string to the console format the value of pi with two digits after the decimal point The final output is then saved in a C-character array.įor example, the following code formats a floating-point decimal with a specified number of decimal points: #include Ĭhar buffer // allocate space for the formatted string The sprintf() function accepts a format string as its initial argument, followed by a varying number of extra arguments, which specify what to insert into the formatted string. In C programming language the sprintf() function is used for formatting strings through the merger of text with variables, numbers, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
